本文共 12098 字,大约阅读时间需要 40 分钟。
文章目录
前言
众所周知,在HDFS NameNode中,一直都有一个老生常谈的难题就是其扩展性的问题,而很多时候我们说HDFS的扩展性问题时我们很多时候都在谈的点在于里面全局锁的问题。一个很通常的场景是NameNode在高并发请求处理下存在着激烈的锁竞争,进而使得用户感觉到他们的请求被处理的有点慢。不过本文笔者不聊关于全局锁优化的问题,最近笔者遇到了另外一种NameNode性能慢的场景,这个事情是发生在锁外的,发生的场景也比较有意思,于是借此机会简单聊聊。
NameNode请求处理慢的场景
我们先来探讨几个能够引发NameNode请求处理慢的场景?
- NameNode处于严重Full GC阶段
- NameNode锁竞争激烈
- NameNode内部用于处理用户请求的Handler持续处于繁忙状态
上述3点是笔者能够快速联想到的场景,除去第一点是JVM层面的优化后,后面两点其实不太好优化,后面两点很多时候是和集群所面临的请求吞吐量有关联。有人可能会说了,上面第三点关于Handler繁忙的状态,我们不可用简单调大NameNode Handler count数量不就可用解决了嘛。调大Handler表面上能够增大throughput,但是这还意味着一个问题:在同一个时间,NameNode内部会有更为激烈的锁竞争问题。锁竞争意味着就会有锁等待。
所以针对上面Handler繁忙的问题,应该从以下几点切入点入手:
Handler为什么处于繁忙状态?Handler在处理 RPC call的某个阶段慢了?是因为在等锁所以导致Handler处理慢?
OK,下面笔者来好好聊聊笔者遇到的Handler处理慢的问题。
RPC返回response的Handler处理慢问题
在笔者遇到的生产场景中,时不时就会出现NameNode callqueue满的情况,但是它的process time其实并没有显示出特别慢的迹象。在最一开始,笔者也是自然怀疑的是NameNode锁的问题,后来经过了一系列的锁局部优化后,还是偶尔会遇到NameNode慢的问题。
这个时候,我们采用了一样profile利器:async-profile,来帮助我们一探究竟。
于是我们发现了一段开销较高的doResponse阶段,
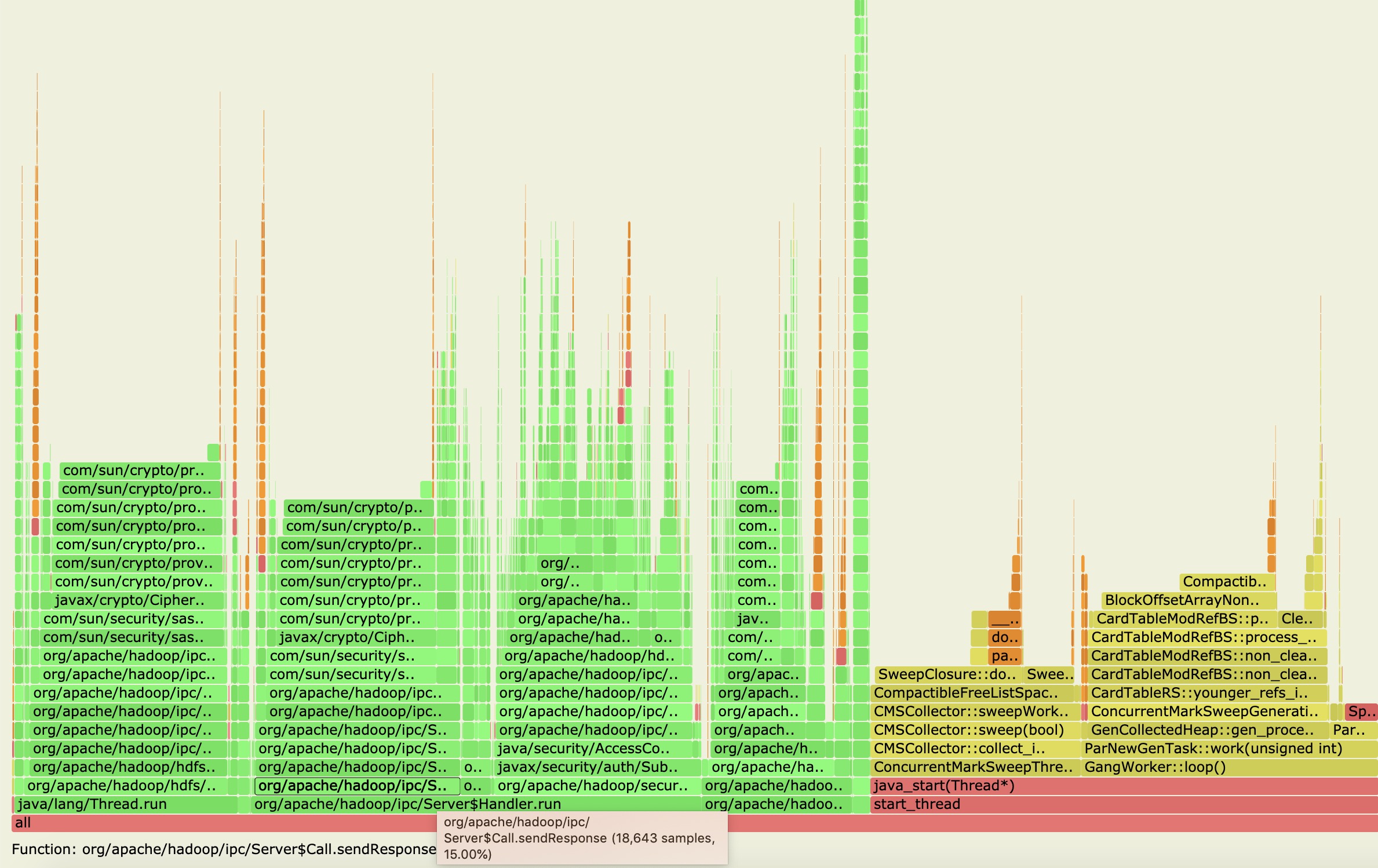 从上图中,我们果然捕捉到了Handler的run方法处理阶段,然后我们再点击进入里面详细的堆栈信息方法,如下图所示:
从上图中,我们果然捕捉到了Handler的run方法处理阶段,然后我们再点击进入里面详细的堆栈信息方法,如下图所示: 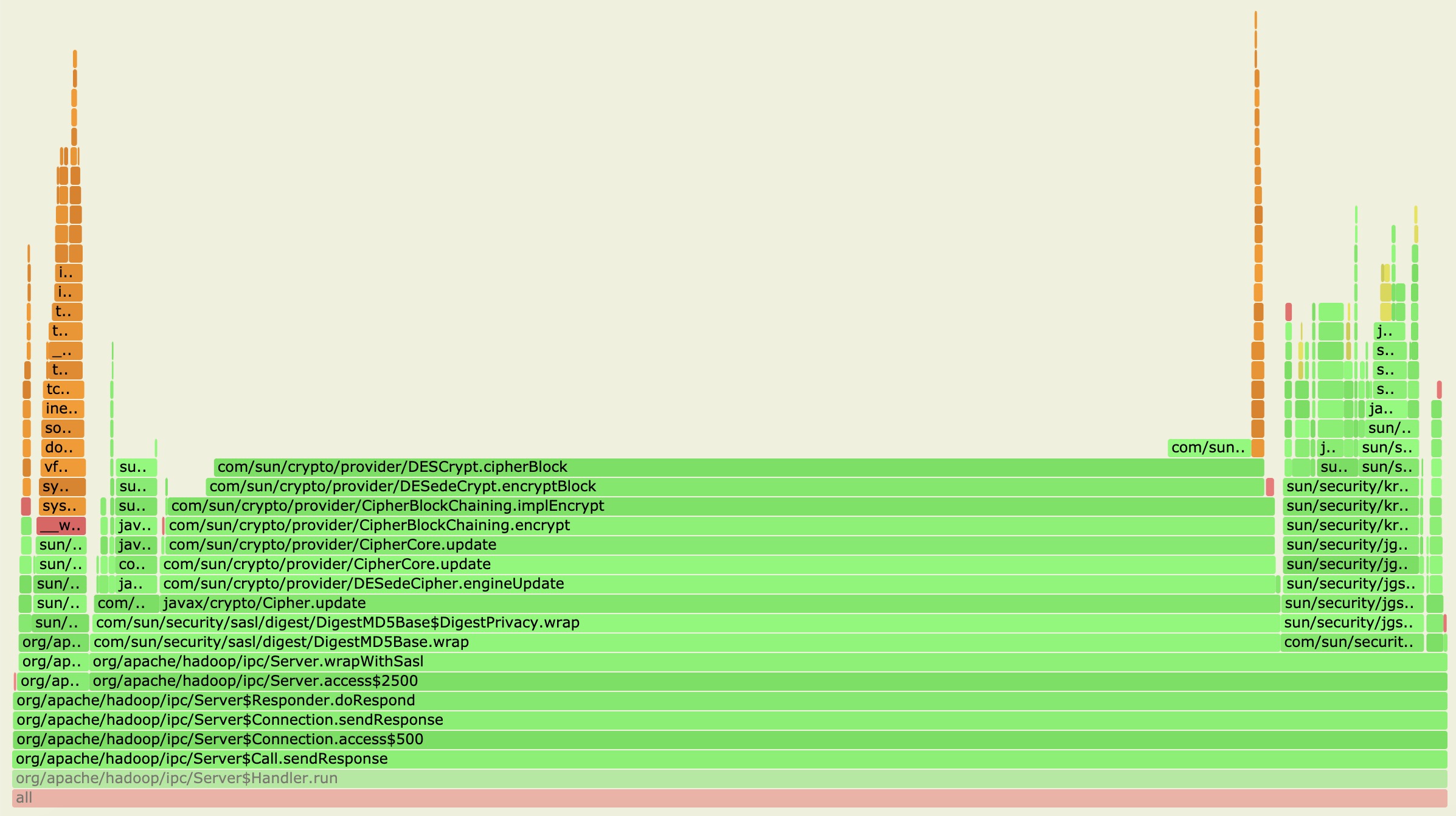
从上图中,我们可以得到许多有用的信息点:
- Handler慢发生在返回response的操作里面,这个阶段已经是在锁外了,在RPC处理完毕之后了已经。
- Response返回操作里面又是主要花在了加密返回信息内容的步骤上。
这里需要说下背景,笔者的这个集群环境是开启了Security模式的,所以会有response加密的过程。一般集群如果没有开启安全认证这些的话,这步骤估计是没有的。
OK,找到了问题的根源后,我们立马想到了下面两项action:
- 第一点,是否有可能改进或替换现有的response加密算法,提升其加密效率。
- 第二点,是否能够将返回response阶段进行异步处理,不去阻塞Handler的处理。
鉴于第一种方法涉及到加密算法的改动,risk比较高,因此我们先考虑采用第二点的方法。还有一点是,第二点提到的特性在实际代码中已经可以支持,async editlog就是用了Hadoop RPC Server底层这个异步response特性来做的。现在的问题其实是如何让正常RPC call处理也能走异步response的方式,目前的HDFS RPC response返回都是同步的。
HDFS RPC call异步response改造
接下来,笔者仿照async editlog的处理方式,对局部RPC call进行了试验改造。
以下是相关核心代码的改动,主要仿照了HDFS-9198 IBR异步线程处理加上HADOOP-10300 RPC call postpone的处理逻辑。
首先定义好postpone线程专门处理这样的延时response call,
/** * The flag that if we should skip the handle by PostponeRpcCallThread. * This is only used for testing. */ @VisibleForTesting static boolean SKIP_POSTPONE_HANDLE = false; /** * Whether to enable async rpc call response. If we enabled this feature, * the rpc call response will be postponed return to client side. */ private boolean asyncResponse; /** * The thread specified for dealing with postponed rpc calls. */ private PostponeRpcCallQueueProcessingThread postponeRpcCallThread;
然后在这个线程内,会设置一个队里来存放需要延时返回response call的队列,外加一个加call进队列的方法和处理队列的方法操作。
/** * The thread specified for dealing with postponed rpc calls. */ private class PostponeRpcCallQueueProcessingThread extends Thread { private final BlockingQueue postponeRpcCallqueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1024); private static final long MAX_LOCK_HOLD_MS = 4; private long lastFullTime = 0; PostponeRpcCallQueueProcessingThread() { super("Postpone Rpc call processor"); setDaemon(true); } @Override public void run() { try { processQueue(); } catch (Throwable t) { ExitUtil.terminate(1, getName() + " encountered fatal exception: " + t); } } ,,, /** * Insert rpc call to be postponed response. * @param call * @throws InterruptedException */ private void enqueue(Server.Call call) throws InterruptedException { if (!postponeRpcCallqueue.offer(call)) { long now = Time.monotonicNow(); if (now - lastFullTime > 4000) { lastFullTime = now; LOG.info("Postpone rpc call queue is full."); } postponeRpcCallqueue.put(call); } }} 接下来我们看看这里NameNode如何加入RPC call进队列,笔者这里取了getBlockLocations这个call做为测试,
/** * Get block locations within the specified range. * @see ClientProtocol#getBlockLocations(String, long, long) */ LocatedBlocks getBlockLocations(String clientMachine, String srcArg, long offset, long length) throws IOException { final String operationName = "open"; checkOperation(OperationCategory.READ); GetBlockLocationsResult res = null; FSPermissionChecker pc = getPermissionChecker(); readLock(); try { checkOperation(OperationCategory.READ); res = getBlockLocations(pc, srcArg, offset, length, true, true); } catch (AccessControlException e) { logAuditEvent(false, operationName, srcArg); throw e; } finally { readUnlock(operationName); } ... postponeResponse("getBlockLocations"); return blocks; } /** * Postponed current rpc call response. * @param methodName Rpc call operation name. */ private void postponeResponse(String methodName) { // if we don't enabled async response, just return. if (!asyncResponse) { return; } // 获取当前的RPC call,即这里的getBlockLocations call final Server.Call rpcCall = Server.getCurCall().get(); // 触发postponeResponse处理会使得此RPC的response会被延时,只有额外再触发一次sendResponse才会真正执行回复 rpcCall.postponeResponse(); try { postponeRpcCallThread.enqueue(rpcCall); } catch (InterruptedException e) { String message = "Exception while edit logging: " + e.getMessage(); LOG.fatal("Exception while adding postpone rpc call", e); ExitUtil.terminate(1, message); } LOG.info("Add " + methodName + " rpc call into postpone rpc call queue."); } 在getBlockLocations最末尾端加postpone的处理是因为一旦前面执行操作抛出错误,这里不应该做postpone处理,延时处理只作用于正常PRC处理完成的情况下。
OK,最后我们再回到call队列处理的操作,
/** * Process the postpone call queue. */ private void processQueue() { // this only used for the testing if (skipPostponeHandle) { postponeRpcCallqueue.clear(); return; } while (isRunning()) { NameNodeMetrics metrics = NameNode.getNameNodeMetrics(); try { Server.Call call = postponeRpcCallqueue.take(); // batch as many operations in the write lock until the queue // runs dry, or the max lock hold is reached. writeLock(); metrics.setPostponeRpcCallQueued(postponeRpcCallqueue.size() + 1); try { long start = Time.monotonicNow(); do { try { // 此时才执行真正的返回response的操作 call.sendResponse(); LOG.info("Triggered postpone rpc call sendResponse function."); } catch (IOException ioe) { LOG.error("Trigger send response call error", ioe); } if (Time.monotonicNow() - start > MAX_LOCK_HOLD_MS) { break; } call = postponeRpcCallqueue.poll(); } while (call != null); } finally { writeUnlock(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { // ignore unless thread was specifically interrupted. if (Thread.interrupted()) { break; } } } postponeRpcCallqueue.clear(); } 鉴于此Thread是一个仅run在Active service上的服务,所以需要在startActiveService/stopActiveService方法里进行thread的启动和停止。
/** * Start services required in active state * @throws IOException */ void startActiveServices() throws IOException { startingActiveService = true; LOG.info("Starting services required for active state"); writeLock(); try { ... if (asyncResponse) { postponeRpcCallThread = new PostponeRpcCallQueueProcessingThread(); postponeRpcCallThread.start(); } } finally { startingActiveService = false; checkSafeMode(); writeUnlock("startActiveServices"); } } /** * Stop services required in active state */ void stopActiveServices() { LOG.info("Stopping services started for active state"); writeLock(); try { ... if (postponeRpcCallThread != null) { try { postponeRpcCallThread.interrupt(); postponeRpcCallThread.join(3000); } catch (InterruptedException ie) { } } initializedReplQueues = false; } finally { writeUnlock("stopActiveServices"); } } 与此对应的unit test测试类代码,server端postpone行为对于client的影响就是block其请求结果的返回。
/** * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one * or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file * distributed with this work for additional information * regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file * to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the * "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance * with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */package org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode;import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.CommonConfigurationKeys;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.*;import org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocol.LocatedBlocks;import org.junit.Assert;import org.junit.Test;import java.io.IOException;import java.net.SocketTimeoutException;/** * The unit test for PostponeRpcCallQueueProcessingThread handling. */public class TestPostponeResponseHandling { private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(TestPostponeResponseHandling.class); private Configuration conf = null; private MiniDFSCluster cluster; @Test public void testEnableRPCResponsePostponeHandling() throws IOException { FileSystem fs = null; Path file = null; try { FSNamesystem.SKIP_POSTPONE_HANDLE = true; conf = new Configuration(); conf.setBoolean(DFSConfigKeys.DFS_NAMENODE_ASYNC_RESPONSE_ENABLED, true); conf.setInt(CommonConfigurationKeys.IPC_CLIENT_RPC_TIMEOUT_KEY, 10000); cluster = new MiniDFSCluster.Builder(conf).numDataNodes(3).build(); cluster.waitActive(); fs = cluster.getFileSystem(); file = new Path("/testEnableRPCResponsePostponeHandling"); DFSTestUtil.createFile(fs, file, 100, (short) 1, 12345L); final DFSClient client = cluster.getFileSystem().getClient(); try { client.getLocatedBlocks("/testEnableRPCResponsePostponeHandling", 0, 100); Assert.fail("The call getLocatedBlocks should be timeout and failed."); } catch (Exception e) { LOG.error("Client getLocatedBlocks error", e); Assert.assertTrue(e instanceof SocketTimeoutException); } } finally { if (fs != null) { fs.delete(file, true); } cluster.close(); } } @Test public void testDisableRPCResponsePostponeHandling() throws IOException { FileSystem fs = null; Path file = null; try { FSNamesystem.SKIP_POSTPONE_HANDLE = false; conf = new Configuration(); conf.setBoolean(DFSConfigKeys.DFS_NAMENODE_ASYNC_RESPONSE_ENABLED, true); conf.setInt(CommonConfigurationKeys.IPC_CLIENT_RPC_TIMEOUT_KEY, 10000); cluster = new MiniDFSCluster.Builder(conf).numDataNodes(3).build(); cluster.waitActive(); fs = cluster.getFileSystem(); file = new Path("/testDisableRPCResponsePostponeHandling"); DFSTestUtil.createFile(fs, file, 100, (short) 1, 12345L); final DFSClient client = cluster.getFileSystem().getClient(); LocatedBlocks blocks = client.getLocatedBlocks( "/testDisableRPCResponsePostponeHandling", 0, 100); Assert.assertNotNull(blocks); } finally { if (fs != null) { fs.delete(file, true); } cluster.close(); } }} 以上改动均在FSNamesystem类内。笔者在测试集群内已经可以跑通上述的异步response的改动,但是还没有在生产环境测试其实际的功效。本文多次提及的RPC postpone处理可详细参阅笔者之前的文章:。RPC postpone的处理并不是完全没有缺点的,server延时response同时意味着server会延时释放与client的connection,简单来说就是server要hold住比之前更多的连接数了。
转载地址:http://lyng.baihongyu.com/